Details of Collinear sets
Using the Hit Filter, or right click in the hit region, set the highlighting for Collinear Sets.
As shown below, the number of highlighted collinear hits and number of collinear sets will be shown in
the Information box.
|
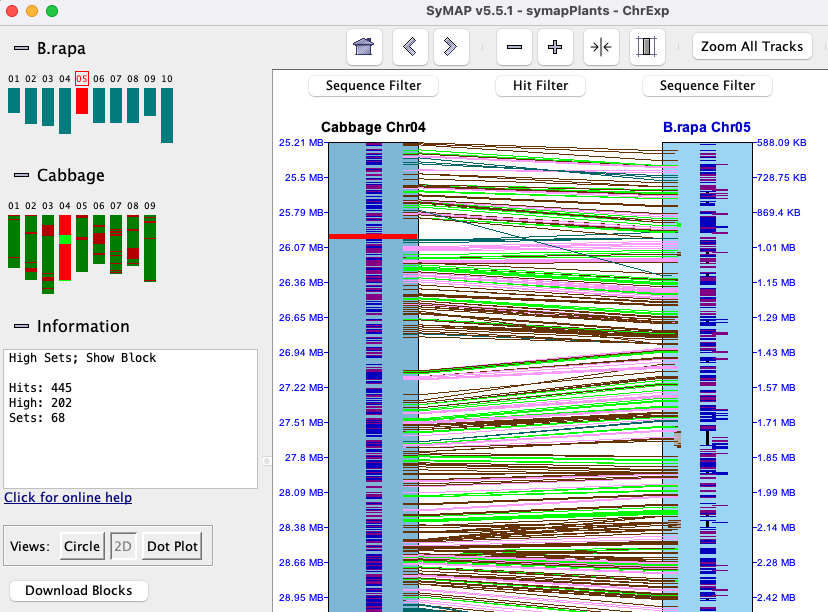
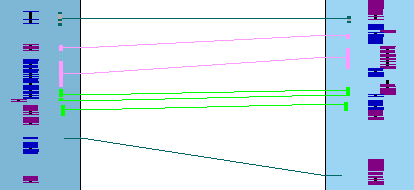
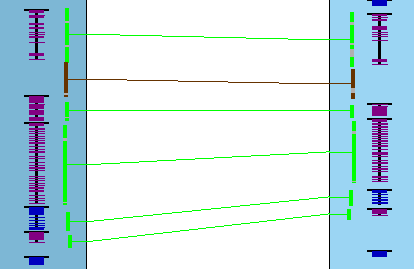
In the image on the right, two different sets are shown (green highlighted hits is the 1st set,
pink is the 2nd). They were broken up by a gene on each chromosome
that do not have a hit.
Forward (=) vs reverse (!=) sets:
a = hit is to the strands (+/+) or (-/-),
a != hit is to the strands (+/-) or (-/+).
All hits in a set are either to the same strand (=) or opposite (!=).
In the image on the right, all genes in both sets are on the same strand.
In the image below, all genes are on opposite strands.
The collinear set algorithm does not consider the amount of overlap of the hit to a gene, or the similarity
of the hit sequences.
|
|
The following are examples of interpreting the 2D view:
|
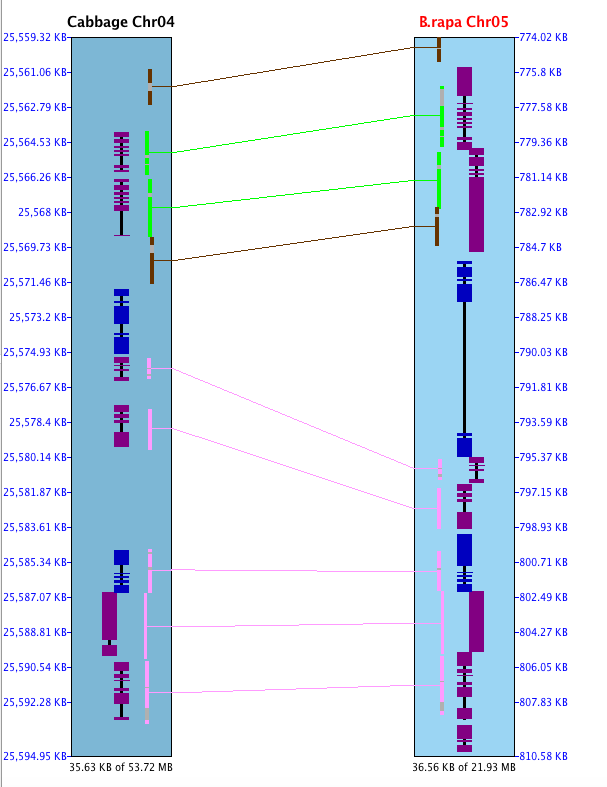
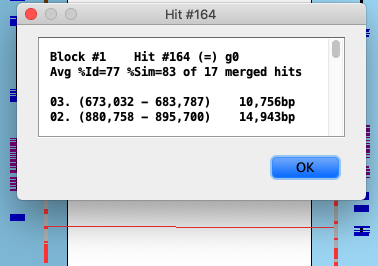
Sometimes a hit looks like it overlaps a gene, but the gene is actually in the gap, so it is not hit.
This is illustrated on the right, where the 3 genes at the bottom appear hit by the red hit wire,
but in fact are spanned by the gap gray area. Note that the
hit popup shows it is a g0 hit (hits no genes).
|
| | |
| |
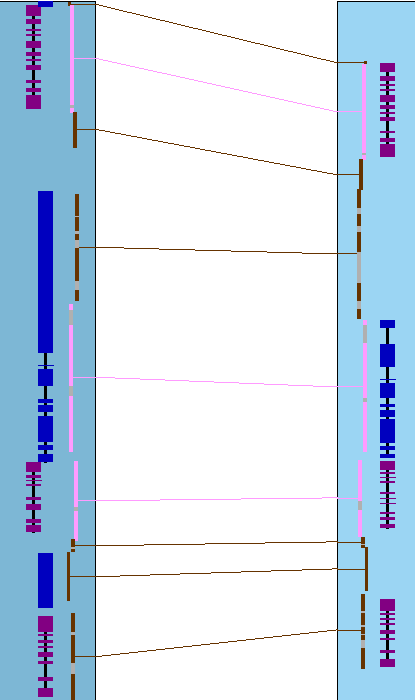
The image on the right shows one collinear set with 6 brown hit wires that are not part of the set. The following
explains them, using the symbols g0 (hits 0 genes), g1 (hits 1 gene), g2 (hits paired genes, at
least one on each chromosome).
| 1 | g1 | Ignored, not part of the set since it does not hit paired genes.
| | 2 | g0 | Ignored.
| | 3 | g1 | Ignored since the same gene has a hit to a paired gene.
| | 4 | g0 | Ignored.
| | 5 | g1 | This ends the set since it does not hit a paired gene.
| | 6 | g2 | This could start a new set, but is not followed by another paired gene.
|
As shown earlier, sometimes two genes look as one, so the Gene Delimiter option is important to
view these.
|
|
Release v5.5.6
The collinear algorithm was improved for release v5.5.6.
|
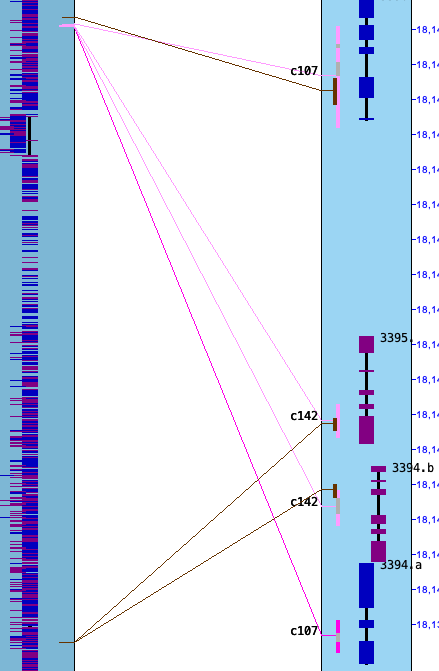
Pre-v5.5.6 gave obviously wrong results if a gene from the hit numbered project
(the hits are numbered along the alphabetically lesser project name) was part of two different collinear sets. An example
is on the right.
In my test sets, this happened a few times between Arabidopsis, Brassica rapa, and cabbage, but none for my partial
mammalian test set of humans, chimps, mouse and rabbit.
|
|
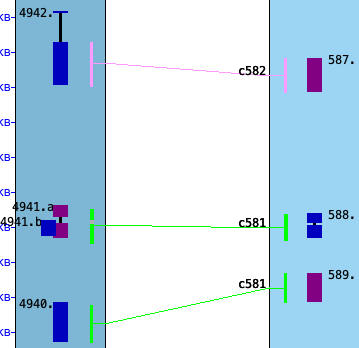
| Referring to the image on the right (from the demo), pre-v5.5.6 called this one collinear set, ignoring the
extra embedded gene 4941.b; v5.5.6 breaks it into two sets due to gene 4941.b (as shown in the image).
|
|
V5.5.6 finds more collinear sets and longer ones. However, since there may be some hit-gene configuration that the algorithm
did not take into account, it verifies all sets and prints an "Error in set x" to the terminal if there is a problem;
albeit, it cannot verify that none are missed (but detailed inspection has not shown any missed ones).
Please email Cari at symap@agcol.arizona.edu if you find any problems.
Go to Top
|









