|
|
|
|
Input files
| Project Directory | Sequence | Annotation | Go to top |
The input is one or more FASTA files of chromosome or scaffold sequences, with optional GFF formatted annotation file(s).
| → | As of v5.5.7, NCBI and Ensembl files can be loaded directly. See Tested genomes for results on loading the files directly. |
| → | The data behaves better in SyMAP if the files have been converted by xToSymap;
see NCBI and Ensembl.
|
| → | If you are using files from another source, see Other. |
Project directory
Put your input files in a directory under: symap_5/data/seq/<project-name>.- The
project-name should be a short descriptive name containing only alphanumeric characters, periods, underscores and hyphens; do not use symbols like %, $, spaces, etc. The names are case-sensitive, so you cannot have "Mus" and "mus" for two different projects. - The
project-name is used in the results directory name and MUMmer output file names. For example, the alignments between demo_seq and demo_seq2 are in directory data/seq_results/demo_seq_to_demo_seq2 and a MUMmer results file is named demo_seq_f2.demo_seq_f1.mum. - You should not rename this directory after the data is loaded into SyMAP! However, you can
define a
Display Name in the project's Parameter to be used in the symap displays, which can be change at any time.
Sequence files
The sequence file(s) must be FASTA format with one or more sequences. For the FASTA format, the name of a sequence is the string immediately following the ">", e.g.>Chr3 Oryza Sativa GAATTCGAATTTGGGTAATGCTAATCAATACAGGTCAAAATCTATGTATTGAGTGGAATATACTGCAAAGTAATTACCTT CTTCCAAAGGAAAGCATTCCTTCTCTCTTGTGGGACTAGCAGATGATCTCGCAGCCAAGACGTGACCACCCAAGGCTCAC ...In this example, the sequence name is "Chr3" and the chromosome 3 sequence follows. The additional information "Oryza Sativa" is ignored.
Important points in naming sequences for SyMAP:
| A. |
Sequence names can only contain letters, numbers, and underscores.
Note: the GFF3 description allows [a-zA-Z0-9.:^*$@!+_?-|]; a sequence name (seqid) must be renamed if it contains any character [.:^*$@!+?-|]. |
| B. | The sequence names must exactly match those used in the annotation files (first column), or the annotations will not be loaded. |
| C. | Use a consistent prefix such as "Chr" for all sequences, then set 'Group prefix' to the prefix in project's Parameter panel. |
| D. | If there is not a consistent prefix, you may leave the 'Group prefix' blank; beware, this can have unintended results, so should be avoided if possible. Make the names short so they will not clutter the display. You may need to rename your sequence, in which case, it must be done in the FASTA and GFF files. |
| E. |
The |
Masking: Decide whether the sequences need to be repeat masked.
- SyMAP does not perform the repeat-masking so it must be done with another program.
However, you may obtain masked sequences from NCBI or Ensembl.
- NCBI provides soft-masked sequences where the
xToSymap NCBI interface provides the option to change it to hard-masked. - Ensembl provides both soft and hard-masked sequences.
- NCBI provides soft-masked sequences where the
- Masking reduces alignment time and false-positive hits, but also runs a risk of concealing true hits due to inaccurate masking. Masking is not really necessary unless the genome is highly repetitive and those repeats are shared with other genomes being aligned. Repeats cause particular trouble for self-alignments.
- Occasionally, MUMmer fails aligning sequences (see MUMmer, which explains detection and solutions for known reasons for failure).
Another masking option, which is available if you have gene
annotation, is to mask out everything but the annotated genes. You
can enable the
Annotation files
Annotation files should be in gff3 format, which is a tab-delimited file of 9 columns.| The first column must exactly match the sequence names in the FASTA files. | |||||
| The third column determines how SyMAP uses the entry.
Only types 'gene', 'mRNA', 'exon', 'gap' or 'centromere' are recognized. | |||||
The last column contains "keyword=value" pairs describing the annotation.
| |||||
| Each mRNA and its exons must come after the parent gene and before the next gene.
The mRNA must be before its exons, but it is okay if all the mRNAs for a gene are listed first. Exons are entered in the order they are found; they must be either ascending or descending. |
For example (extracted from Ensembl gff3 file):
1 araport11 gene 11649 13714 . - . ID=gene:AT1G01030;Name=NGA3;.... 1 araport11 mRNA 11649 13714 . - . ID=transcript:AT1G01030.2;Parent=gene:AT1G01030.... 1 araport11 three_prime_UTR 11649 11863 . - . Parent=transcript:AT... 1 araport11 exon 11649 12354 . - . Parent=transcript:AT1G01030.2.... 1 araport11 CDS 11864 12354 . - 2 ID=CDS:AT1G01030.2;Parent=transc... 1 araport11 CDS 12424 12940 . - 0 ID=CDS:AT1G01030.2;Parent=transc... 1 araport11 exon 12424 13173 . - . Parent=transcript:AT1G01030.2.... 1 araport11 five_prime_UTR 12941 13173 . - . Parent=transcript:AT... 1 araport11 exon 13335 13714 . - . Parent=transcript:AT1G01030.2.... 1 araport11 five_prime_UTR 13335 13714 . - . Parent=transcript:AT... 1 araport11 mRNA 11649 13714 . - . ID=transcript:AT1G01030.1;Parent=gene:AT1G01030.... 1 araport11 three_prime_UTR 11649 11863 . - . Parent=transcript:AT... 1 araport11 exon 11649 13173 . - . Parent=transcript:AT1G01030.1.... 1 araport11 CDS 11864 12940 . - 0 ID=CDS:AT1G01030.1;Parent=transc... 1 araport11 five_prime_UTR 12941 13173 . - . Parent=transcript:AT... 1 araport11 exon 13335 13714 . - . Parent=transcript:AT1G01030.1.... 1 araport11 five_prime_UTR 13335 13714 . - . Parent=transcript:AT...The following information will be saved in the SyMAP database for this record, where the exons are associated with the gene via a MySQL index:
1 gene 11649 13714 ID=AT1G01030;Name=NGA3;rnaID=AT1G01030.2;desc=.... 1 exon 11649 12354 1 exon 12424 13173 1 exon 13335 13714
xToSymap Interface
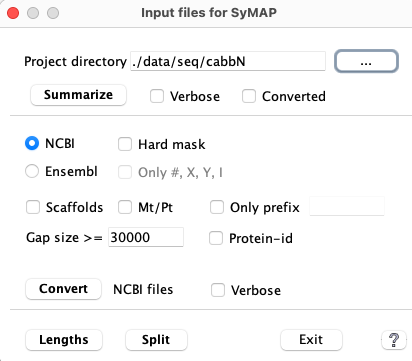
| Interface | Summarize | Convert | Lengths | Split | Go to top |
| 1. | Summarize | This will output basic statistics. Run this first to make sure your input is valid. |
| 2. | Convert | The |
| 3. | Summarize
with | Run this to make sure that the conversion worked as you expected.
This shows the sequence prefixes, and can be used to set the |
| Optional. The following run on the files in the | ||
| 4. | Lengths | Run it to see if you need to set a |
| 5. | Split | Splits the converted file |
NOTE: The NCBI and Ensembl files have variations and I may not have accounted for them all. If
Summarize
- Directly under the project's directory, e.g.
symap_5/data/seq/cabb Brassica_oleracea.BOL.dna_sm.toplevel.fa.gz Brassica_oleracea.BOL.59.gff3.gz - The project's ncbi_datasets/data/<sub-directory>, e.g.
symap_5/data/seq/cabb/data/seq/ncbi_dataset/data/GCF_000695525.1 GCF_000695525.1_BOL_genomic.fna genomic.gff - The project's sub-directories /sequence and /annotation, e.g
symap_5/data/seq/cabb sequence/ genomic.fna annotation/ anno.gff
The GFF file must end in .gff or .gff3 (with optional .gz).
The following is an example terminal and log file output:
------ Summary for ./data/seq/cabbN ------
Log file to ./data/seq/cabbN/xSummary.log
Sequence directory: ./data/seq/cabbN/ncbi_dataset/data/GCF_000695525.1 29-Jul-2024 10:16
GCF_000695525.1_BOL_genomic.fna
Annotation directory: ./data/seq/cabbN/ncbi_dataset/data/GCF_000695525.1
genomic.gff
FASTA sequence file(s)
Example header lines:
Chr: >NC_027748.1 Brassica oleracea var. oleracea cultivar TO1000 chromosome C1, BOL, ...
Scaf: >NW_013617415.1 Brassica oleracea var. oleracea cultivar TO1000 unplaced genomic ...
Mt: >NC_016118.1 Brassica oleracea mitochondrion, complete genome
Count Totals:
9 Chromosomes
32,876 Scaffolds
1 Mt/Pt
32,886 Total sequences
Count Prefixes:
32,876 NW_
10 NC_
Counts of Length Ranges:
32,284<10k 552<100k 41<1M <10M 5<50M 4<100M
488,954,160 Total length
GFF Annotation file(s)
Summary:
44,386 Genes from 49,563 (use protein_coding only)
44,382 mRNAs from 56,687 (44,382 has protein_id)
227,191 Exons from 398,922
Gene Attribute:
44,386 Dbxref 44,386 ID
44,386 Name 569 end_range
7 exception 44,386 gbkey
44,386 gene 44,386 gene_biotype
81 locus_tag 7 part
985 partial 499 start_range
mRNA Attribute:
44,305 product
Input type: NCBI chr NC_ prefix; NCBI GFF header
NCBI 'gene_biotype' keyword; NCBI mRNA 'product' keyword
------ Finish summary for ./data/seq/cabbN/ ------
Observations:
| 1. | The last line confirms that the |
| 2. | It shows that there are 9 chromosomes to be converted to symap files. |
| 3. | It confirms that an mRNA and exons are found for each protein-coding gene. |
| 4. | On the first example line, it has 'chromosome C1'. Since the 'chromosome' is followed by 'C1' instead of a digit (i.e. 1), the chromosome identifier will be 'C1' in the conversion. |
| 5. | After conversion, the summary will be like this
log file.
There is a remark that the file may be hard-masked, which was not done by the |
Verbose
The Ensembl cabbage files- From FASTA:
- Base count (maximum 2,147,483,647 bases).
- Lengths of 5 sequences.
- From GFF:
- The first gene, mRNA and exons lines.
Types , e.g. gene, mRNA, and exon.Gene Attributes biotype , e.g. protein_coding.
As shown in Tested genomes, it appears to be more common not to have a letter before the chromosome number (e.g. chromosome 1), in which case the chromosome identifier will be Chr01. For example, for Homo sapiens, see NCBI summary log compared to the Ensembl summary log (both are
zgrep ">" [use your FASTA file name]
Convert
| 1. | Select |
| 2. | Select the options you want; see NCBI or Ensembl options. |
| 3. | Select |
Lengths
The FASTA files must be in the project'sSummary: If your file has many small scaffolds and you just want to process the large
ones, the summary will help you decide what to you as the project's
Parameter
Values for parameter 'Minimal length' (assuming no duplicate lengths): #Seqs Minimum length 10 550,871 20 193,719 30 152,041 40 122,531 50 98,180 60 85,914 70 70,524 80 65,697 90 61,049 100 58,280If you set the minimal length at 550871, SyMAP will process the 10 largest sequences.
Split
The input files are:sequence/genomic.fna annotation/anno.gffThe function will do the following:
- Split genomic.fna into a separate file per chromosome, and put all other sequences in scaf.fna. The genomic.fna file is deleted when done.
- Split anno.gff into a separate file per chromosome, and put all other sequences in scaf.gff. The anno.gff file is deleted when done.
General
| Editing the convert scripts | Tested genomes | Go to top |
Editing the convert scripts
- The convert scripts are in the symap_5/scripts directory called
convertNCBI.java and convertEnsembl.java.
- Move the one you want to change to the symap_5/data/seq directory, as
it must be run from there.
- Once you make your changes, execute: javac ConvertNCBI.java
You will need to have JDK installed to use the javac command. - To run your compiled script: java ConvertNCBI <project directory name>
These scripts are simply written, using only standard operations found in all major languages.
Tested genomes
In Aug 2024, the scripts were tested on the following:| Genome | NCBI | Ensembl | Sequence bp in file | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arabidopsis thaliana (thale crest) | Chr 1-5 | Chr 1-5 | 119M | |
| Brassica oleracea (wild cabbage) | C1-C9 | C1-C9 | 489M | C prefixes chr# |
| Oryza sativa (rice) | Chr 1-12 | Chr 1-12 | 386M | |
| Prunus persica (peach) | G1-G8 | G1-G8 | 228M | G prefixes chr# |
| Prunus yedoensis | Scaffolds 4015 | N/A | 319M | Draft |
| Caenorhabditis elegans (worm) | Chr I,II,III,IV,X | Chr I,II,III,IV,X | 100M | |
| Bemisia tabaci (whitefly) | Scafs 19,750 | Contigs 227 | 615M | |
| Danio rerio (zebrafish) | Chr 1-25 | Chr 1-25 | 52,633M | Contains 930 ALT CHR |
| Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit) | Chr 1-21, X | Chr 1-21, X | 2,841M | |
| Homo Sapiens (human) | Chr 1-22, X, Y | Chr 1-22, X, Y | 3,298M |
See Times for more about tested genomes and the compute time.
To load the originals files into SyMAP, the following was done:
- Create /sequence and move the FASTA file into it.
- Create /annotation and move the GFF file into it.
- Run the
xToSymap Summarize andLengths functions.- For both NCBI and Ensembl, a Minimal length was set that would just load the chromosomes.
- For NCBI, an option was to set the Group prefix to 'NC_' to load the chromosomes only.
For example, for species such as Homo Sapiens, if Group prefix or Minimal length were NOT specified, over 500 sequences got loaded. With Ensembl, it also had a problem with duplicate entries because it has scaffold names such as HSCHR19KIR_CA01-TB04_CTG3_1 and HSCHR19KIR_CA01-TB01_CTG3_1, where the name was truncated at the "-", hence, HSCHR19KIR_CA01 is a duplicate name.
- Ensembl Danio rerio (zebrafish): It could not be loaded without conversion.
It has 1922 sequences where most of them had prefix "ALT", the word 'chromosome' in their header line,
and were the size of their REF chromosome,
so setting a Minimal length did not exclude them. And there was no unique chromosome ID prefix to use as
the Group prefix in
symap .
- Ensembl Oryza and NCBI Arabidopsis were aligned and synteny computed. There was no problem with the Synteny, but the Arabidopsis names cluttered the displays, and there were many attributes for each.
- NCBI Mus musculus and Homo Sapiens were converted/split and their Chr17 successfully aligned.
Exceptions to load the converted files into SyMAP: The above downloaded genomes were all converted with the defaults, with the following exceptions:
- Ensembl Danio rerio (zebrafish): The 100's of 'Alt' sequences appear as valid chromosomes,
hence, the
Only #,X,Y,I option was used.
- Ensembl Bemisia tabaci (whitefly): The words 'chromosome' or 'scaffold'
were NOT part of the header lines. The header line ID prefix was 'Contig',
hence, the
Prefix only ='Contig' was used; the output used the sequence ID prefix 'Unk'. ThenLengths was used to determine aMinimal length to enter onsymap project Parameters.
- NCBI Bemisia tabaci (whitefly): Only had scaffolds, so using
Include Scaffold was necessary. ThenLengths was used to determine aMinimal length to enter onsymap project Parameters.
- NCBI Prunus yedoensis:
The words 'chromosome' or 'scaffold'
were NOT part of the header lines. The header line ID prefix was 'CPJQY' (not the NCBI prefix of 'NC_'),
hence, the
Prefix only ='CPJQY' was used; the output used the sequence ID prefix 'Unk'.
- Cabbage had 'C' before its chromosome number so the chromosome names were C1, C2, etc.
Peach had 'G' before its chromosome so the chromosome names were G1, G2, etc. .
Input variations: There are probably more variations then shown here, which may possibly be handled with the
Ensembl
| Go to top |
Email Comments To: cas1@arizona.edu