> Instructions
To open the query interface, first select two or more projects in the Project Manager. Then select the|
The Notes:
Open the | 
|
> Query Setup
| Rules | 1. General | 2. Single genes | 3. Pair hits | 4. Compute Groups | Go to top |
Rules
| Setup | Hit#, Gene# | Pseudo | Wait/Stop | Go to top |
Setup
|
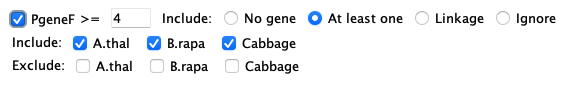
Set the desired filters and then select 1. Most filters can be used in conjunction with other filters; options will be disabled if they cannot be used with a selected filter. 2. 3. | 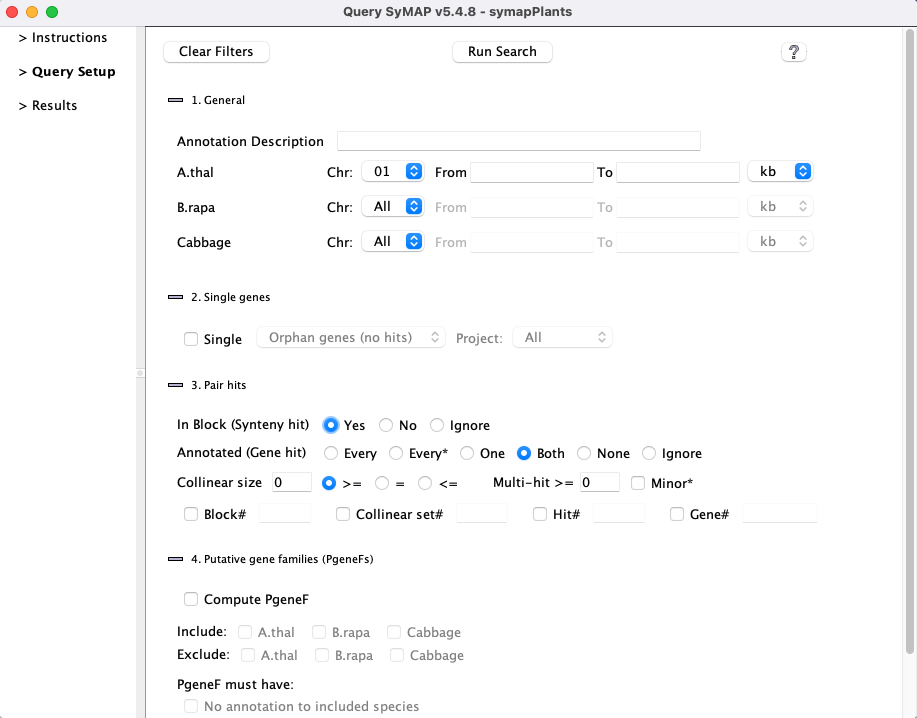
|
| All | 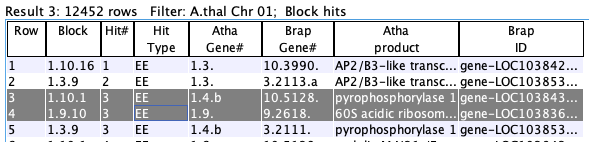
|
|
Gene#
All genes have a
|

| |
|
Not numbered: The Numbered: These are numbered sequentially, where the counts start after the annotated gene numbers,
hence, providing a unique | 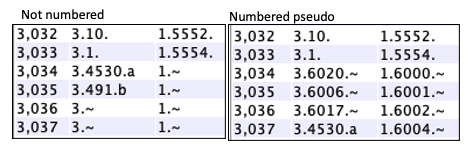
|
Wait/Stop Query:
→ Wait for the current query to stop running before starting another!
It is not possible to start a new query from the same panel, but you could start one from a different table;
they both will fail, so do NOT do this!
|
→ When a query is running, you will see a status line and the |

|
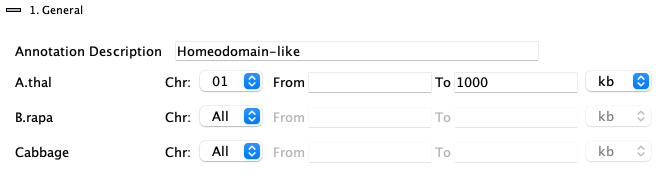
1. General
Enter a substring: the entire |
|
| Select a specific chromosome for the species. | ||
| The | ||
| The |
It is valid to enter only the
Caveats:
- The
From andTo are disabled forSingle genes ,Block# ,Collinear set# ,Hit# , andGene# . - If more than one chromosome is selected in conjunction
with
Gene# ,Multi orCluster , theRun Query will popup a message that is it not allowed, and stop.
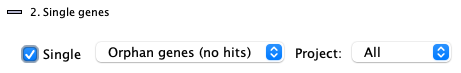
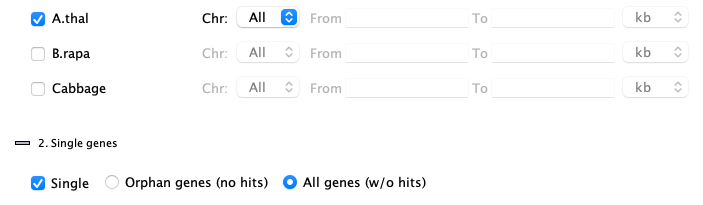
2. Single genes
| The |
|
Orphan genes (no hits)
Genes that do not a have a hit and meet the additional filters. The orphan genes are relative to the projects shown on theInstruction page. For example, if species X, Y and Z have synteny computed between all pairs, but only X and Y are selected, the orphan genes for X would be those with no hits to Y. If X,Y&Z are selected, the orphan genes for X would be those with no hits to Y and Z.
All genes (w/o hits) , i.e. genes with and without hits
This shows all genes that meet the additional filters, regardless if they have a hit or not. There is always the same set of genes for a project, regardless of synteny.
| Unselect species: When the |
|
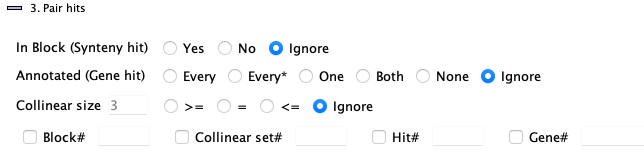
3. Pair hits
| Block | Annotated | Collinear size | Hit >= | Exact | Go to top |
|
Each hit connects two species (projects) and hence represents a pair of aligned
regions for two of the selected species.
Filters are as follows: |
|
| Only hits that are part of a synteny
block will be returned. All hits will have a value for the | |||
| Only hits that are NOT part of a synteny
block will be returned. No hits will have a value for the |
|
| Only hits that align to a gene on one or both sides of the hit will be shown.
The | |
|
| This is like the | |
|
| Only hits that align to a gene on ONE end will be shown.
The | |
|
| Only hits that align to genes on BOTH ends will be shown.
The | |
|
| Only hits that do NOT align to a gene on either end will be shown.
The | |
| If a species chromosome is selected with | ||
|
| List all hits in collinear sets that have size >= N or = N or <= N, respectively. | |
|
| Do not filter on collinear set sizes. | |
| See Collinear, which explains the SyMAP collinear sets. | ||
this should not be used if one project is un-annotated. |
| For the following 4 filters, do not include the 'Chr' number. Instead use the chromosome pull-downs (from | |
|
Enter a single block number (the Narrow the search by using the chromosome pull-downs, as shown in the examples below.
| |
| Enter a set number (the Narrow the search by using the chromosome pull-downs. | |
| Enter a hit number. Both major and minor gene hits will be shown.
Narrow the search by using the chromosome pull-downs. | |
Enter a
| |
4. Compute Groups
| 1. Multi-hit genes | 2. Cluster genes | Go to top |
These two options are computed on the fly.
They produce query results with values for the
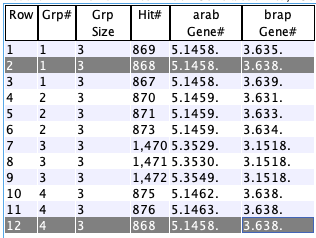
4.1. Multi-hit genes

List all genes that have
- The target gene refers to the gene with >= N hits to the opposite species.
- The target must be a gene, but it can be to un-annotated hits on the opposite species, regardless if they are numbered pseudos.
Use the
Both genes filter to exclude them. - These can be pre-filtered by species chromosome (only one can be selected),
%Sim , etc. - See Multi-hit Gene Report... for a good way to see a condensed view of the results.
- See Statistics for the summary.
The options are as follows:
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||
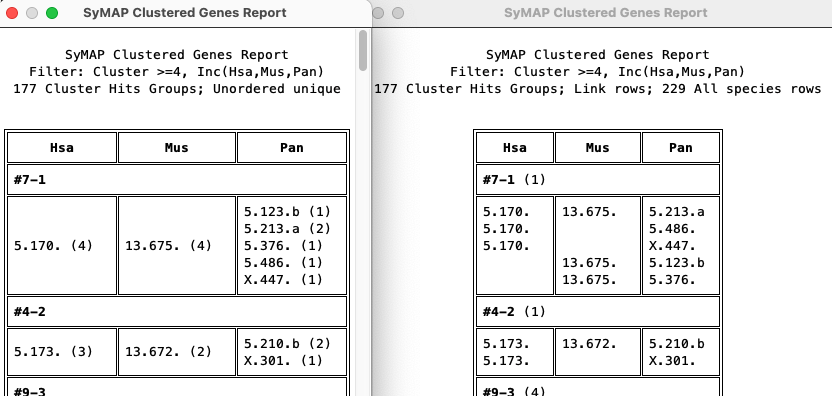
4.2. Cluster genes
This algorithm was updated in v5.7.9; the old one did not provide complete results.
- This algorithm finds clusters of overlapping genes. That is, every gene in the cluster aligns to at least one other gene in the cluster, and all genes that align to any gene in the cluster are included.
- Each cluster is given a group number, which is shown in the Query Results table (column name
Group ). - These can be pre-filtered by species chromosome (only one can be selected),
%Sim ,%Olap , etc.
Note: the hits are first filtered on these values, then clustered. For example, if the hits are filtered on%Sim >=80, and theExclude option is used, clusters will be shown that do NOT have hits with%Sim >=80 in the excluded species. - Pseudo (un-annotated) will be included if they are number.
UseBoth genes to exclude pseudo; useOne gene to only show gene to pseudo. - Beware: huge clusters can be created!!!
- For large databases, it is wise to first try filters as described in item 3 and 4.
- The algorithm does not save any clusters that have >20,000 hits.
- In order to show all clusters regardless of size, start
viewSymap -ac ; note, it may run out-of-memory creating the clusters, and theCluster Report probably will not finish gracefully.
- See Cluster Report... for a good way to see a condensed view of the results. This also will show totally linked clusters.
The N entered will apply to whichever of the following options is selected: |

|
| The cluster must have at least N hits, and it must contain at least one gene from each included species. | |
| The cluster must have at least N genes from each included species. A better N may be 2, as the default 4 is a big requirement. |
| If there is more than two species, the following options will be present: | |
| The clusters are created, and then any cluster without at least one gene from each included species is removed. | |
| The clusters are created, and then any cluster with at least one gene from an excluded species is removed. | |
| Neither | If a species is not |
Alternative algorithm:
|
If you start |
|
Result Panel
| 1. Results table | 2. Columns | 3. Statistics | 4. Top buttons | Go to top |
1. Results Table
A pair hits table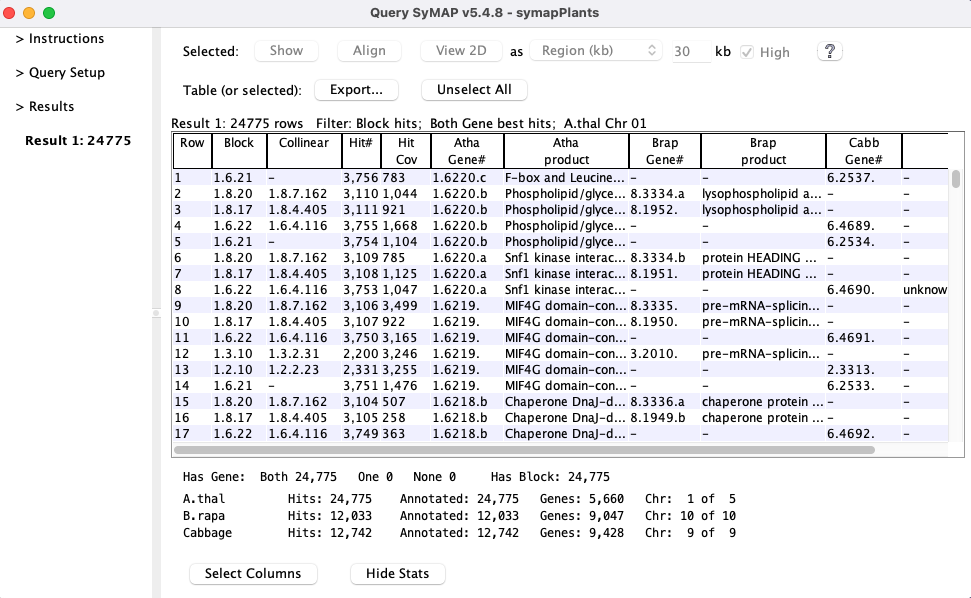
Pair hits :- The table contains columns for all of the selected species, but each hit only connects two species, and the other species columns are empty.
- Each
Hit# is only listed once unless minor genes are included (see Rules) or the hits are in clusters. - A gene may be listed more than once if it has multiple hits.
Single genes :- If the query specified
Single genes, then each row represents one gene and shows data only for one species.
- If the query specified
You can sort the columns by clicking the column name in the table, and rearrange them by dragging the
column name. You can add/remove columns using the
2. Columns
| 1. Pair hits columns | 2. Single gene columns | 3. Auto-save columns | Go to top |
| The buttons on the bottom will be | 
|
| Clears the selection of all columns except | |
| Selects the default columns, which are shown in the image above. If the collinear query was run, this will include the Collinear. If the group query was run, this will include the Group. | |
| Arranges similar columns, putting the gene columns first. |
In the column panel shown above, hover over a column name to see its brief description. Following are the full descriptions of the columns.
2.1 Pair hits columns
| Row number. This column does not sort and should stay checked. | ||
| The synteny block containing this hit (if any). The format is Chr.Chr.Block#, where the two "Chr" are chromosome numbers. | ||
| The number of hits which comprise the synteny block. | ||
| The collinear set containing this hit (if any). The format is Chr.Chr.Size.Set# (e.g. 1.2.5.100; there are 5 adjacent gene hits in set# 100 on Chr1 to Chr2). | ||
| The number assigned to the hit. They are sequential along the chromosome of the alphabetically lesser species, e.g. Arab<Brap. | ||
| Percent identity of the alignment. The value of the "Identity" column is from the MUMmer file. If the hit has subhits, then this is an approximation. | ||
| Percent similarity of the alignment (as determined by the BLOSUM scoring matrix). The value of the "Similarity" column is from the MUMmer file. If the hit has subhits, then this is an approximation. | ||
| The number of subhits in a clustered hit. | ||
| If the two ends have signs "+/+" or "-/-", this will be "==".
If the two ends have signs "+/-" or "+/-", this will be "!=". Note: to see the actual values, | ||
| The summed subhits within a clustered hit taking into accounts overlaps. The summed subhits are usually different for the two sides; this will be the longest. | ||
| There are two alternative algorithms for clustering the hits on database creation, which assign
different hit types, as follows:
e.g 'EI' would indicate the hit covers A.thal exon and Cabbage intron. | ||
|
| ||
| Chromosome of the hit. | ||
| Start and end of the annotated gene. The | ||
| The gene number is C.#.{a-z}. The C is the chromosome number. The # is the sequential number along the chromosome. If a run of genes overlap, they receive the same gene number with different suffixes {a-z, a2-z2, etc}. | ||
| Start and end of the hit region. | ||
| Hend-Hstart+1 | ||
| The value depends on which In order to view the gene overlap instead, start | ||
| They all have a | ||
| There are also columns for each keyword in the | ||
| See GFF Attributes for modifying the keywords shown. | ||
2.2. Single genes columns
The single genes table only has the| This is the number of hits to the gene in the ENTIRE databases, including SELF synteny. |
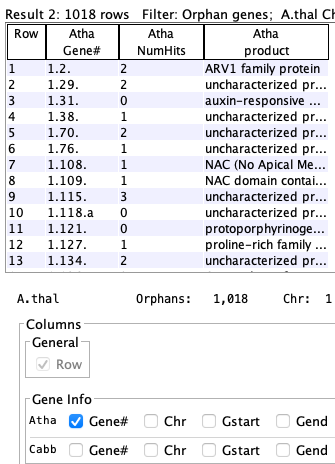
Arab-Cabb orphans
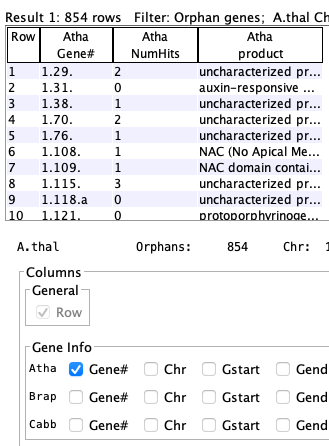
| Arab-Brap orphans
| Arab-Brap-Cabb orphans
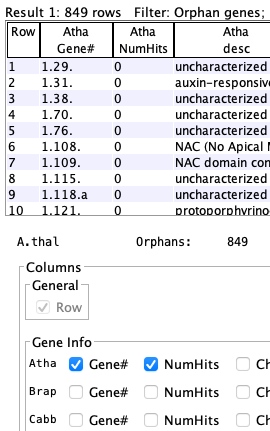
| Gene #1.2 is an orphan for Arab-Cabb but has a count of 1 because it is not an orphan in Arab-Brap; i.e. it is not listed in the Arab-Brap table because it has a hit. |
2.3 Columns and order shown
During a SyMAP session, when you display a new table, it will use the columns and order from the last table created or modified (add/remove columns).The selected columns are saved between sessions (described below), but the order is not.
2.4 Auto-save columns
The columns selection is saved in a file called .symap_saved_props in the user's home directory so that the next time youIf you have multiple SyMAP databases, when you change between them the columns displayed are relative to the last SyMAP database queried (they may seem some what random to a different SyMAP database).
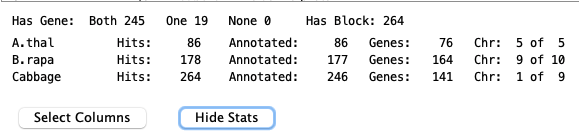
3. Statistics
Statistics for the query results are shown at the bottom of the results table. They can be hidden by selectingMost of the statistics are self-explanatory except the following:
For
A.thal Groups: #50 (50) #142 (192) B.rapa Groups: #618 (810) #984 (1794) Cabbage Groups: #847 (2641) #495 (3136) | There are 3,136 total groups.
A.thal has 50 with B.rapa and 142 with Cabbage, where the first set is 1-50, the second is 51-192, etc. |
4. Top buttons
| 1. Show | 2. MSA... | 3. View 2D | 4. Export... | 5. Report... | 6. Search... | Go to top |
The
4.1 Show
For the selected row, a popup will show all columns and associated information for the hit. The text in the popup can be copied.4.2 MSA...
Below is an image of a multiple alignment. The right half shows the sequence, where the first row is the consensus: A 'n' (purple) is used where there is no majority base. Lowercase (green) is used if there is a least one mismatch.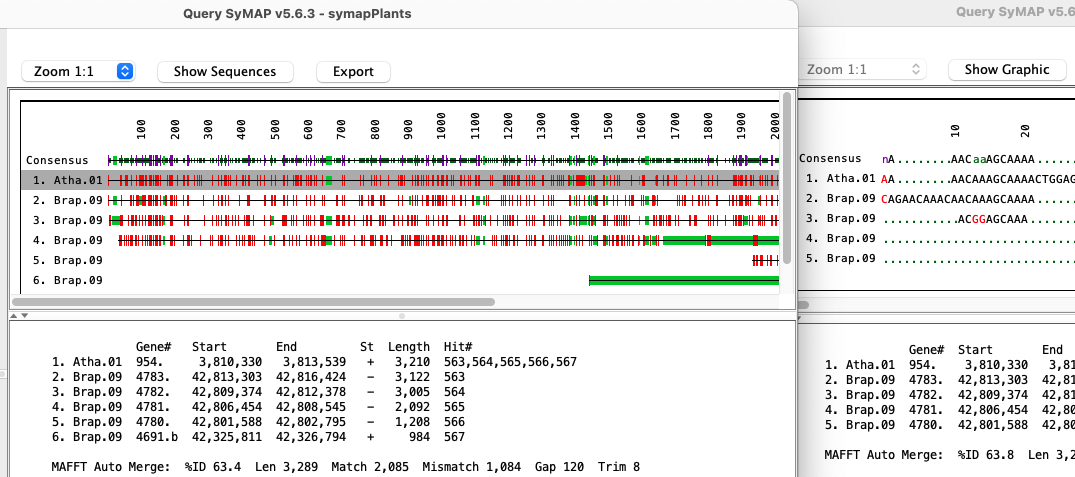
Select one or more rows from the query table. The sequences of the selected hit(s) are written out and a multiple alignment is created using either MAFFT (Katoh 2013 MBA:30) or MUSCLE (Edgar 2004 NAR:32). MAFFT can be run with multiple CPUs and the optional --auto option, where --auto takes longer but allows MAFFT to determine the best algorithm to use.
| 
|
| While aligning, the line at the top of the panel will state the number
of bases aligned as shown on the right.
The |
General Notes:
→ Wait for the current MSA to stop running before starting another!
It is not possible to start a new MSA from the same table, but you could start one from a different table;
they both will fail, so do NOT do this!
→
- Their processes will be called muscle for MUSCLE and distbfast for MAFFT; MAFFT may have some other process running, but distbfast seems to be the one that takes the most time/memory.
- To stop: you can type
top at the command line, copy the 'process number' beside distbfast or muscle, then at the terminal, type kill -p 'process number'. - Make sure distbfast or muscle are stopped, as they take a lot of memory!
However, if you do not see it, then it has completed.
MAFFT Notes:
→ All executables were removed that did not seem necessary. However, I may have removed
one(s) that are used in certain unusual situations when --auto is used. Try again with --auto unchecked.
→ On Mac, if you are using MAFFT --auto, you may get a "Cannot be verified" for dndpre.
See MacOS and external programs to fix this.
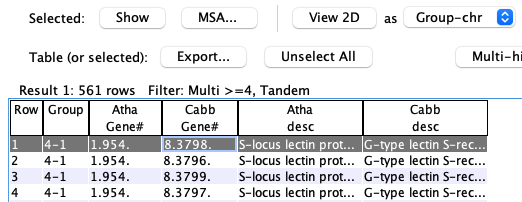
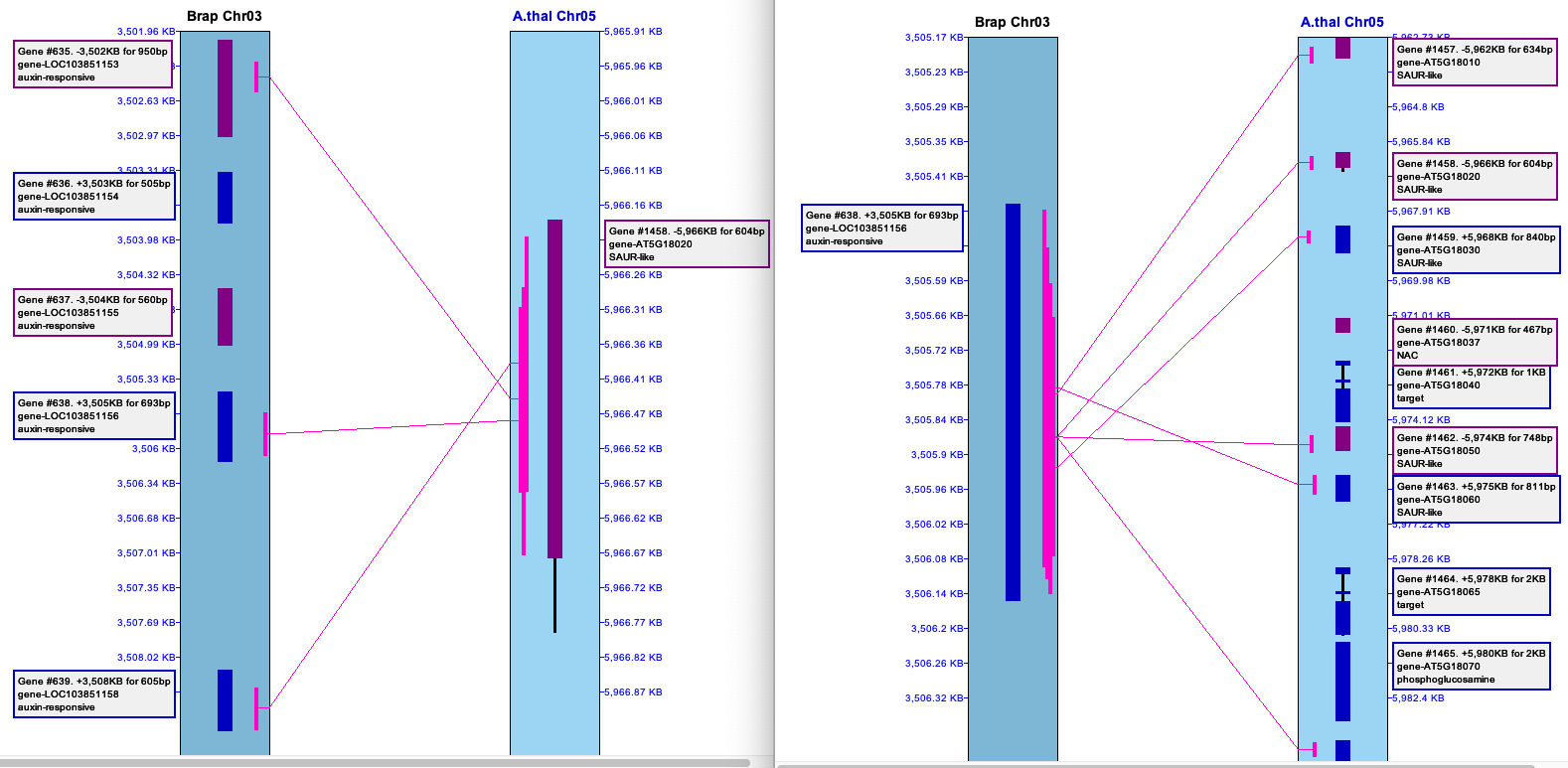
4.3 View 2D

This displays the
| Option | Column1 | Selected Hit | Hit Filter |
| N/A | The hit is padded on each side by the amount indicated in the | ||
| The entire collinear set of hits for the selected hit will be shown. | |||
| The entire synteny block for the selected hit will be shown. | |||
| The entire group of hits of the selected hit's group will be shown. |
2CoSet is short for collinear set.
The default value of the pull-down depends on the query performed, with the following precedence:
| If selected, the selected hit is highlighted in the Popup-query color (default magenta).
The coloring can also be turned off by selecting the | |
| If selected, the |
Example:
|
The table below shows results from the The image on the right shows the
The table below shows results when the
It is possible to select two rows for a 3-chromosome | 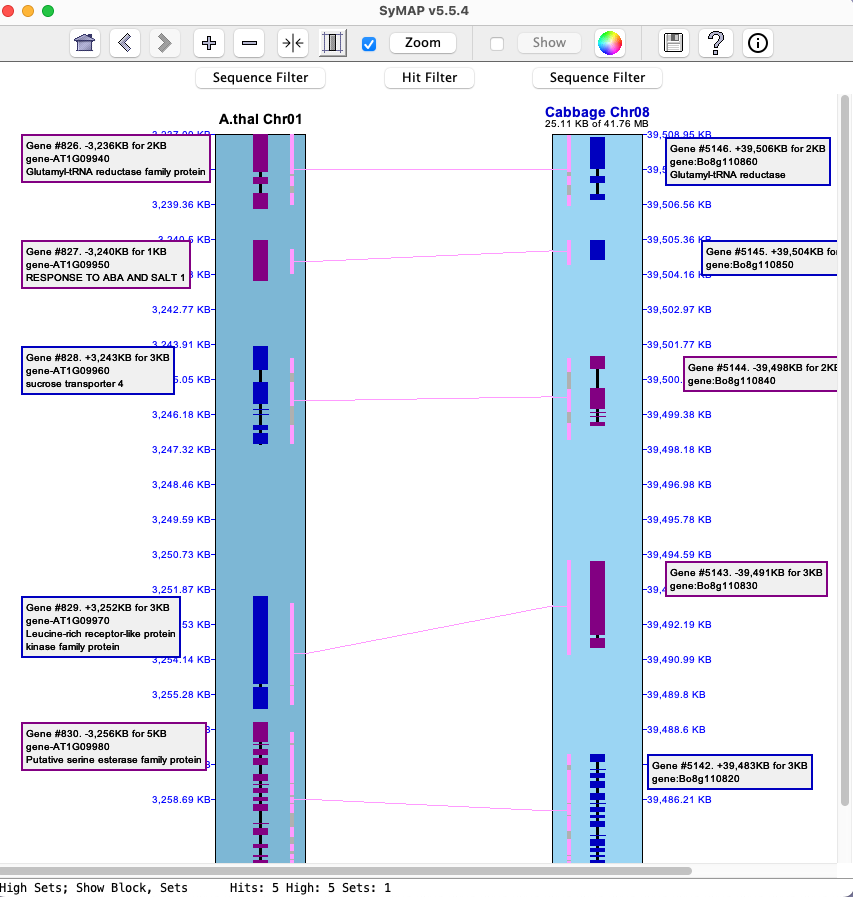
|
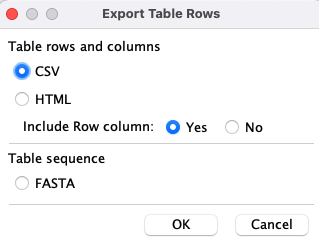
4.4 Export...
One or more rows can be selected for the following exports; or if no rows are selected, the entire table is exported.|
The
|
|
4.5 Report...
| Interface | Gene report | Collinear report | Multi-hit gene report | Cluster gene report | Go to top |
- The report is on the genes in the query table; hits without paired genes are ignored.
- Unless the query is for
Collinear ,Multi-hit orCluster genes , aGene report will be produced. - This is most relevant when used with >2 species. It has not been tested for >4 species.
Gene ,Collinear andMulti-hit genes produce a reference-based report whereas theCluster genes does not; howeverCluster genes shares most of the same options.
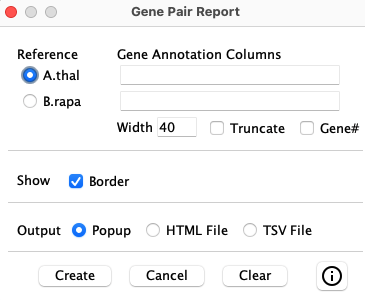
Reference-based Interface
The menu on the lower-right shows the options that will always exist. There may be additional options in between the middle lines, depending on the condition used to create the table, as discussed below.
|
|
|
| Determines the length of the annotation before wrapping around; relevant to long descriptions. | |
| Truncate long description using the width specified. | |
| Show the | |
| Draw a border around each cell of the table. Otherwise, there will only be a line before each group of genes. | |
| Displays a panel of the results, which will look just like viewing the HTML file. | |
| Writes a file that can be viewed as a web page. It is written in a human readable form such that anyone with HTML knowledge can edit it. | |
| Writes a tab-separated-values file that can be viewed with Excel or any editor. | |
Additional options for >2 species: The following options will be shown between the middle lines if there are >2 species. The options are explained with the respective report.
Link: This term is used to indicate that there is a hit between two species, typically non-reference species.
For all reports:
- The reference column is in italics. In the TSV file, the reference header has an '*'.
- The annotations correspond to the genes listed for the species. A "---" indicates that there is a gene with no corresponding annotation. If there is more than one gene in a column, the corresponding annotations will be separated by a ";".
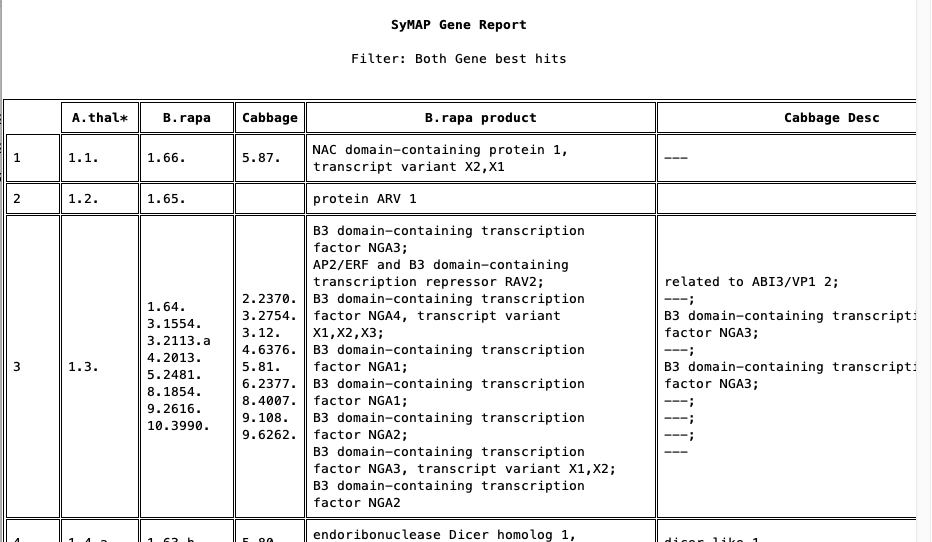
Gene Report
|
| Only show rows with all species. | |
| Only show rows with all species and at least one link. | ||
| Only show rows with links between all species (this often produces no results). | ||
| Show the links. Since | ||
The report lists all genes from the reference species and what genes each aligns to. The image below shows the top of two different
Rows are always merged that share the same reference. The top line shows there are 15 single rows (one gene for each species) and 0 multi rows (multiple non-reference genes for at least one species). There are 2 multi rows in Mus11, where one is shown in the 3rd row.
A "=" indicates that the gene is linked to the gene next to it (ignoring the Reference column); a "+" indicates it is linked to the gene over one column (only happens when there are 4 species).
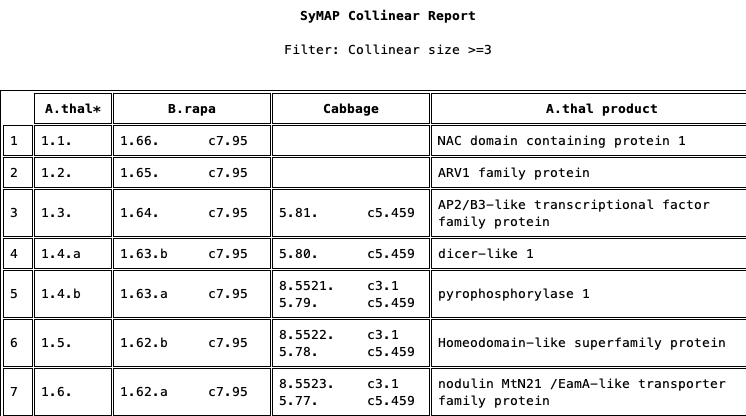
Collinear Report
Collinear sets are grouped to show the union of overlapping sets for the reference gene.| The reference gene must be in a collinear set with every species. | ||
| Displays the collinear set beside each gene. | ||
|
The report on the right shows the first union of the A.thal collinear sets. This was generated with The '1 [3 sets]' indicates it is the first union with 3 collinear sets. For the non-reference gene columns, by default, the collinear set size and number (size.setN) is shown. For example, row 4:
The other genes in each collinear set are obvious since they share the same size.setN, e.g. #8.1 is shown in 8 rows. |
|
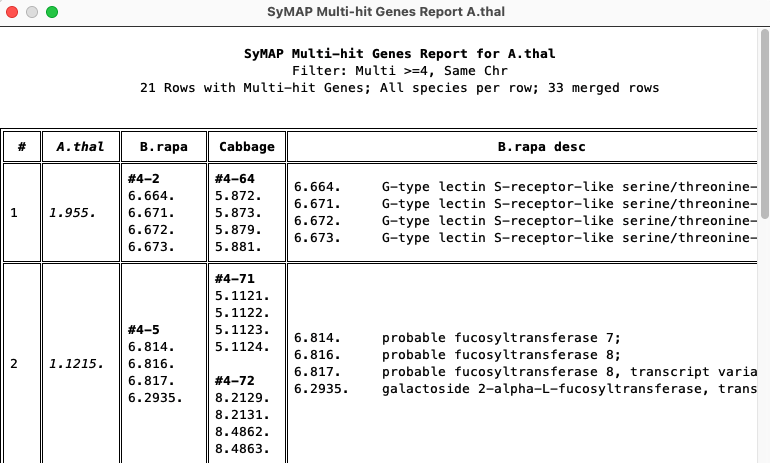
Multi-hit gene report
Shows reference genes that align to at least N genes, where N is the number input on the query panel.| Only show rows with all species. | ||
| Show all rows. | ||
| Show the group (size-number) above the respective. | ||
The
4.5.5 Cluster gene report
The cluster report has no reference, as shown on the right (i.e. no radio buttons for selection).
|
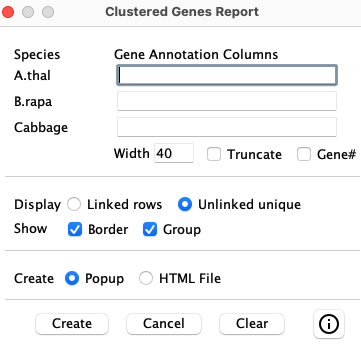
| ||||||||||||
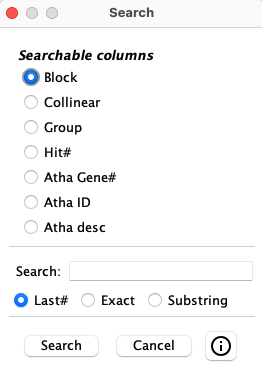
4.6 Search...
| The The columns in the popup will vary depending on the columns displayed in the table.
It will only show the columns that are searchable. Besides the top 4 shown (see image on right),
the species
| 
|
- On the first search, the number M of occurrences of the search string will be found.
- The table will position to the next row with the search string and that row will be selected; a message on the panel will state "Found N of M".
- If you close the window between searches and select it again, it will start where it left off.
- If all rows with the search string have been found, there will be a message on the panel saying "Found all M values".
Changing any value on the panel also restarts the search.
> Results
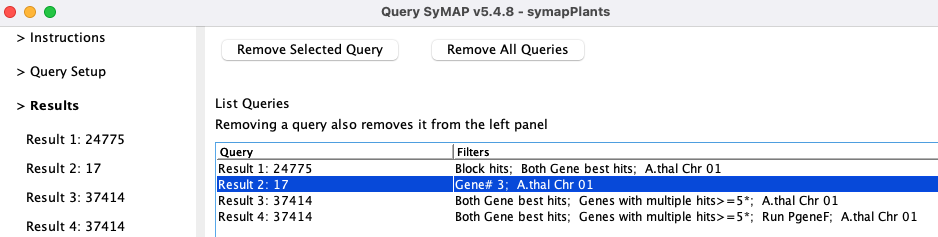
All query results are listed under the
The only way to remove query results from the left tab is by selecting them in this table followed
by
| Go to top |
Email Comments To: cas1@arizona.edu